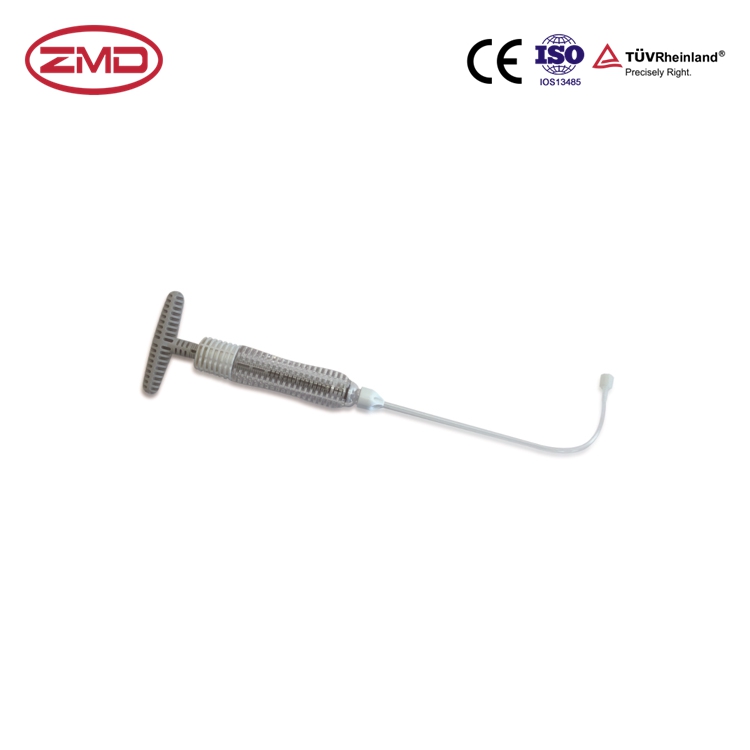
The syringe or pump in a bone cement injection system is a vital component. The bone cement, usually polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), is a remarkable biocompatible material. When it’s delivered to the desired location within the bone, it begins to harden. The syringe is a more traditional option and is manually operated. The plunger of the syringe is pushed to exert force on the bone cement, causing it to flow through the needle or cannula and into the bone. A pump, on the other hand, offers more precise control over the delivery process. It can maintain a consistent flow rate, which is especially important in procedures where the injection needs to be carefully timed and the amount of cement precisely metered. For example, in vertebroplasty, the syringe or pump must accurately deposit the cement into the fractured vertebra to provide the necessary structural support. If the cement is not properly delivered, it may not effectively stabilize the bone, and the patient may not experience the expected pain relief or bone strengthening.
The mixing chamber is a critical part of the system. Bone cement components need to be mixed thoroughly to achieve the right consistency and chemical reaction for optimal strength and setting time. The two – part components of the bone cement, typically a powder and a liquid, are combined in the mixing chamber. The mixing process is not just a simple combination; it’s a carefully controlled chemical reaction. The powder and liquid must be in the correct proportions to ensure that the cement hardens at the right rate. If the mixing is not done properly, the resulting cement may be too weak or may set too quickly or slowly. For instance, if the cement sets too quickly, it might not be possible to complete the injection before it hardens, leading to a failed procedure. Conversely, if it sets too slowly, there’s a risk of the cement migrating out of the intended area before it solidifies.
The needle or cannula provides a direct pathway for injecting the cement into the specific area within the bone. The needle is a slender, pointed instrument that can penetrate the bone’s outer layer and reach the target site. The length and gauge of the needle are selected based on the location and characteristics of the bone being treated. A cannula, which is a tube – like structure, can also be used. It offers more stability during the injection process and can sometimes be left in place for additional procedures or to monitor the injection site. The tip of the needle or cannula is designed to be as atraumatic as possible to minimize damage to the bone and surrounding tissues. In procedures such as percutaneous vertebroplasty, the needle must be carefully inserted through the skin and soft tissues and then into the vertebra. The correct placement of the needle or cannula is crucial to ensure that the cement is injected precisely where it’s needed to provide the most effective bone stabilization.
The control unit is essential for allowing precise control over the injection pressure and flow rate of the bone cement. By carefully regulating these parameters, medical personnel can ensure that the cement is injected smoothly and without complications. The injection pressure needs to be carefully monitored because if it’s too high, there’s a risk of the cement being forced into areas where it shouldn’t go, such as blood vessels or adjacent soft tissues. On the other hand, if the pressure is too low, the cement may not flow properly and may not fill the intended space within the bone. The flow rate also matters; a too – rapid flow rate might lead to improper distribution of the cement, while a too – slow rate could increase the procedure time and potentially affect the quality of the cement’s hardening due to exposure to air or other factors. The control unit uses sensors and feedback mechanisms to adjust the injection process in real – time, making it a crucial safeguard during bone cement injection procedures