AO Type External Fixation
ZMD
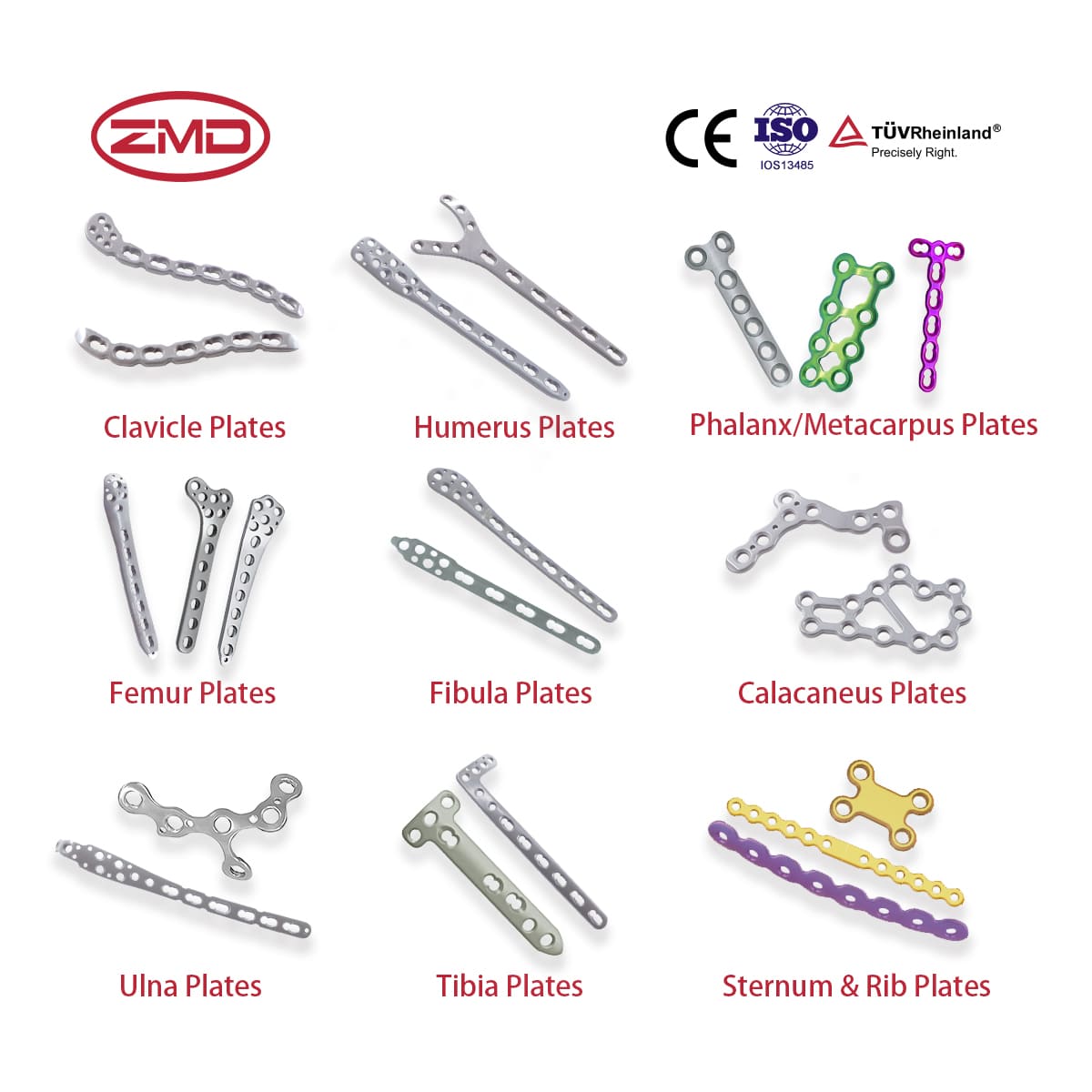
Orthopedic Products
Haven't been able to locate the product you're searching for yet?
If you're interested in more orthopaedic implant products, feel free to get in touch with our ZMD consultants.
What is AO Type External Fixation?
The external frame in AO type external fixation is a crucial part. It usually comprises metal rods and clamps. The rods, often made of stainless steel or titanium, are strong and biocompatible. They offer the primary structural support and can be adjusted in length and angle. The clamps are utilized to connect the rods to the pins or wires that are inserted into the bone.


When is AO Type External Fixation Needed?
AO type external fixation represents a highly adaptable surgical approach that has become an essential asset in the realm of orthopedic treatment. It emerges as a preferred option precisely in those scenarios where the conventional strategies of casting or internal fixation prove to be inadequate or less than optimal. Let’s explore in more detail the specific circumstances in which AO type external fixation is commonly contemplated:
Fracture Management
- Complex Fractures: When fractures present with a multiplicity of fragments or extensive comminution, AO type external fixation frequently takes precedence. The capacity to precisely insert pins into each discrete fragment and then integrate them with the external frame facilitates accurate alignment and reliable immobilization. Take, for example, a severely comminuted fracture of the tibia. Here, the fixator’s pins can be deftly positioned within the numerous broken pieces, and the accompanying frame subsequently secures them, thwarting any errant movement that might otherwise impede the healing trajectory. This stable milieu is indispensable as it affords the body’s innate bone – healing mechanisms the opportunity to generate new bone tissue around the fracture site and methodically reunite the fragments.
- Open Fractures: In the event of a bone fracture accompanied by an open wound, AO type external fixation confers substantial benefits. Owing to its minimally invasive attribute, the pins can be introduced via diminutive incisions in the skin, thereby minimizing further insult to the already compromised soft tissues. The external frame promptly imparts stability to the bone while simultaneously permitting unhindered access to the wound. This allows for efficient cleaning, routine dressing changes, and vigilant monitoring for any telltale signs of infection. The combined effect of these features is a more comprehensive management of both the bone injury and the associated soft tissue damage, ultimately enhancing the patient’s overall prognosis.
- Segmental Fractures: For fractures entailing a segment of missing bone, which may result from severe trauma or a bone tumor resection, AO type external fixators can furnish temporary stabilization. The residual bone segments can be anchored with pins and maintained in position by the external frame, thereby establishing a stable foundation for subsequent procedures such as bone grafting. Consider a scenario where a section of the femur is absent. In such a case, the AO type external fixator can ensure the proper alignment of the two remaining ends of the bone until an appropriate graft can be procured and implanted to restore the bone’s structural integrity.
Deformity Correction
- Angular Deformities: AO type external fixation demonstrates remarkable efficacy in rectifying angular deformities like varus or valgus deviations of bones. The adjustable nature of the external frame empowers the orthopedic surgeon to effectuate gradual and exact modifications in the bone’s alignment over time. For instance, in a child afflicted with a congenital valgus deformity of the tibia, the application of the fixator, followed by a sequence of meticulous adjustments to the frame, enables the application of gentle corrective forces to the bone. Consequently, the bone remodels and straightens progressively, leading to a reduction in the deformity and an improvement in the limb’s alignment and functionality.
- Rotational Deformities: When bones are misaligned in a rotational sense, AO type external fixators can be deployed to address the issue. The pins inserted into the bone segments serve to immobilize them, while the frame is manipulated to rotate the bone back to its normal anatomical position. This is of particular significance in fractures where improper healing has given rise to a rotational deformity or in instances of congenital rotational anomalies in the limbs. For example, if a patient exhibits a rotational deformity of the forearm following a fracture, the AO type external fixator can be utilized to precisely rotate the bones back to their correct alignment during the healing process, thereby guaranteeing proper range of motion and optimal function of the limb.
- Limb Length Discrepancies: In cases where there exists a disparity in limb length, often attributable to trauma, growth disorders, or previous surgical interventions, AO type external fixators can be enlisted in conjunction with distraction osteogenesis techniques. The fixator’s frame can be adjusted to incrementally separate the bone segments, thereby triggering the formation of new bone within the resultant gap.
Blog
International Women’s Day: Salute to the “She – Power” at ZMD
International Women’s Day: Salute to the “She – Power” at ZMD Amid the trends of “Intelligent Medical Devices” and “Minimally Invasive Medical Technologies”, ZMD thrives
Discover Innovation with Sunan Medical at AAOS
Discover Innovation with Sunan Medical at AAOS The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Annual Meeting is the premier event for orthopedic professionals worldwide, offering
Visit Us at Expomed Eurasia 2025: Discover Sunan Medical’s Innovations
Visit Us at Expomed Eurasia 2025: Discover Sunan Medical’s Innovations The 32nd Expomed Eurasia, taking place from April 24-26, 2025, at the Tüyap Exhibition and